
This blog post will explain that how to change file and directories Ownership in Linux using the chown and chgrp commands.
Changing File Ownership
- Only root can change a file’s owner
- Only root or the owner can change a file’s group
- Ownership is changed with chown:
chown {-R} user_name file|directory...
- Group-Ownership is changed with chgrp:
chgrp [-R] group_name file|directory...
File ownership can be changed with the chown command. For example, to grant ownership of the file “test.txt” to amar, the following command could be used:
sudo chown amar test.txt
chown can be used with the -R option to recursively change the ownership of an entire directory tree. The following command would grant ownership of testdir and all files and subdirectories within it to student:
sudo chown -R amar testdir/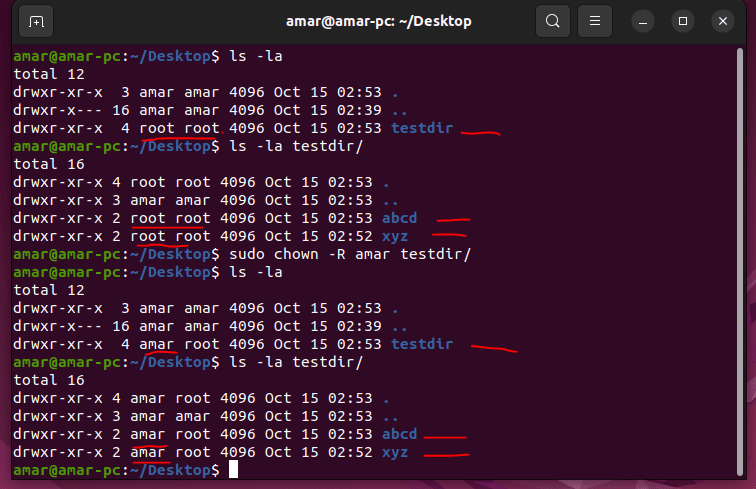
Only root can change the ownership of a file. Group ownership, however, can be set by root or the file’s owner. root can grant ownership to any group, while non-root users can grant ownership only to groups they belong to. Changing the group ownership of a file is done with the chgrp command. The syntax is identical to that of chown, including the use of -R to affect entire directory trees.