
Step-by-step instructions on how to install and configure FTP server in CentOS Linux. Avoid common errors and set up a secure file transfer solution with ease.
What is FTP?
FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, is a standard network protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server.
FTP is a very versatile protocol that can be used to transfer files of any size or type. It is often used to upload and download files to and from web servers, but it can also be used to transfer files between any two computers on a network.
To use FTP, you need to have an FTP client program installed on your computer. FTP client programs are available for all major operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Once you have installed an FTP client program, you can connect to an FTP server by entering the server’s hostname or IP address, username, and password.
Once you are connected to an FTP server, you can browse the server’s directory structure and transfer files between your computer and the server.
FTP is a very efficient and reliable way to transfer files over a network. It is also a very secure protocol, as it supports encrypted connections.
Here are some of the common uses of FTP:
- Uploading and downloading website files: FTP is the most common way to upload and download website files to and from a web server.
- Transferring large files: FTP is a good choice for transferring large files, such as video files or software packages.
- Backing up data: FTP can be used to back up data from one computer to another, or to a remote server.
- Sharing files: FTP can be used to share files with other people over a network.
FTP is a very powerful and versatile protocol that can be used for a variety of purposes. It is a good choice for anyone who needs to transfer files over a network, regardless of the size or type of files.
How to FTP works
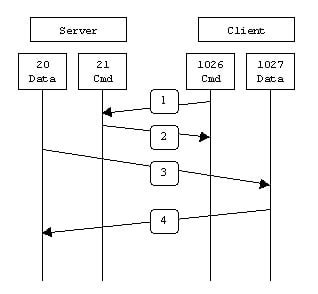
Step a: Client connects to server on port 21.
Step b: Server responds and ask for authentication.
Step c: Client decides whether to connect passively or actively and authenticate with username password).
Step d: If it is an active connection, server opens port 20 for data transfer and gives ftp prompt after successful authentication.
Step e: Client call for file and server initiates file transfer.
Following picture shows a simple way of data transfer through ftp.
Before setting up FTP server we have to clear our self about active and passive ftp
Why FTP uses two ports.
As we already discussed FTP uses 21 ports for control and 20 for data transfer, this is because of many reasons such as
- Separate data transfer path so that you can still use control port do some communication with server.
- Can initiate multiple data connections without control interruptions.
- Server decides when to send data which will minimize any increase of load on server.
Difference between an Active FTP and Passive FTP server
FTP is a tricky protocol which uses two ports one as command port (21) and other as data port (For active FTP it is 20 and for passive port it is grater then 10000). So, it boils down to which port is used for data transfer.
We will set-up and configure ftp server in CentOS 6.7. This procedure is same for all Redhat based distributions like Centos, Fedora, Scientific Linux, Oracle Linux etc.
Installing FTP server in Centos
Step 1: We will use below host name and IP address for our test machine to setup FTP server
Server IP: 192.168.0.9
Host Name: ftp.linuxnix.com
Just edit file /etc/hosts
#vi /etc/hosts
and add the line on bottom and save
192.168.0.9 ftp.linuxnix.com
Step 2: Install vsftpd (very secure FTP daemon) package.
#yum install vsftpd ftp
Configuring FTP server in Linux Centos
Step 3: Configure vsftpd package. We will edit /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf you can do this with gedit (If installed) or vi command.
#vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
Change the line which contain anonymous_enable=YES to anonymous_enable=NO. This will permit any one to access FTP server with authentication.
anonymous_enable=YES
Uncomment the following line
local_enable=YES allow users in /etc/passwd to login
write_enable=YES allow users to write files. “NO” will permit only to read.
Change the line chroot_local_user=NO to chroot_local_user=YES. This will permit local user as FTP account. If you add an user, it will be treated as a FTP account as well.
The local user directory will be the FTP directory.
chroot_local_user=YES
Save the file.
Step 4: Permit Home user to FTP account
Permit FTP account directory as user home directory.
#setsebool ftp_home_dir on
Step 5: Open firewall or IP Table update so that our FTP server is accessed through 21 port.
We can do this with one of the two ways.
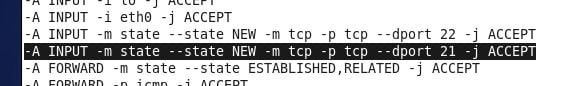
a) First Way: Edit the file /etc/sysconfig/iptables and add the line (Like the picture)
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 21 -j ACCEPT
than
#service iptables restart
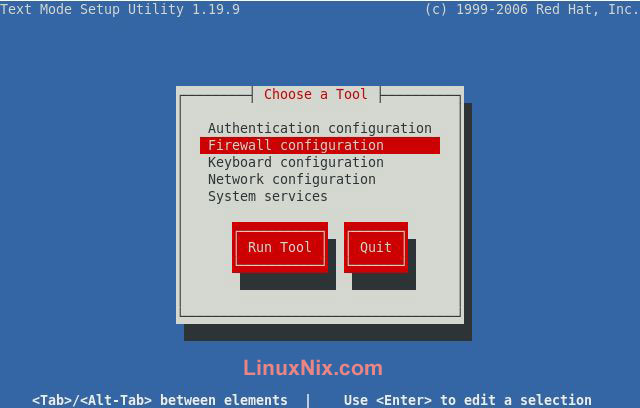
b) or Second way: Through setup command.
#setup
Than the screen will come as shown below.
Select FTP
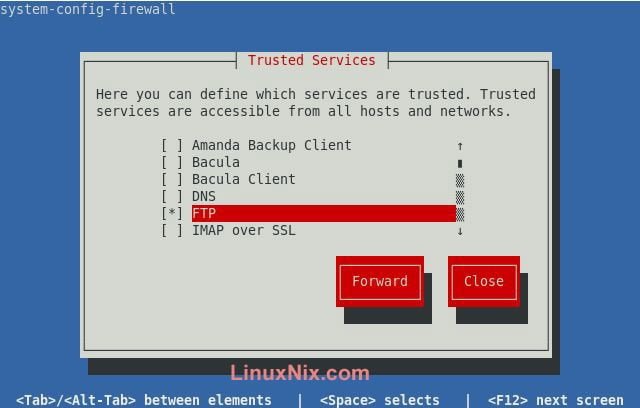
Save
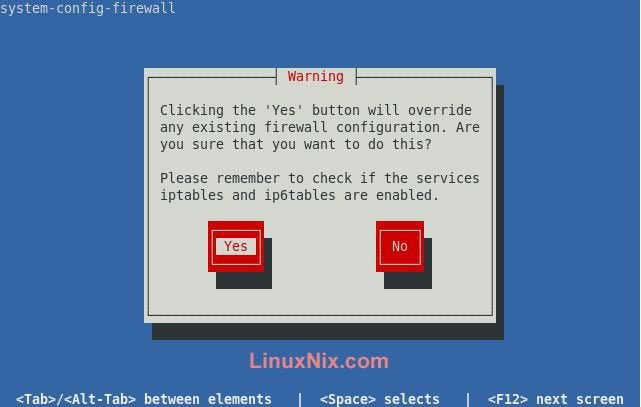
Actually this will add the above line to iptables file.
Step 6: Start FTP service once you do all the above edit’s.
#service vsftpd start
To enable this service at boot time, you have to execute below chkconfig command.
#chkconfig vsftpd on
Step 7: Now the FTP server is live. We can check with ftp command. Just create a test account to do the testing.
#useradd linuxnix
#passwd linuxnix
Changing password for user rejaul.
New password:
Now we will login to ftp
ftp ftp.linuxnix.com
# ftp localhost
Trying ::1...
ftp: connect to address ::1Connection refused
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost (127.0.0.1).
220 (vsFTPd 2.2.2)
Name (localhost:root): lftp ftp.linuxnix.com
331 Please specify the password.
Password:
230 Login successful.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
Now FTP server is ready and you do multiple file transfers from FTP as well. You can also browse your ftp server from web browser after typing below line in address bar.
ftp://ftp.linuxnix.com
Username and password will be asked. Then you will find the file and directory tree.
